
Linear drives are one of the three primary applications for BRECOflex timing belts, and with it comes its own unique set of challenges. Helping our customer find the best solutions is how our engineering staff spends the bulk of their time and expertise. Commonly, a customer will come to us with a linear drive application and have a predetermined timing belt in mind. Our job is to ensure that they are making the best choice.
Linear drives convert linear rotary motion into linear motion and timing belts are one of the a crucial component of linear drives. Sounds simple enough but there is much to consider. Finding the solution that yields a high accuracy drive that runs with peak performance is the goal for every application.
For starters, there are several types of linear drive configurations including open linear drive, vertical closed linear drive, t-pulley linear slide and omega drives. There can actually be situations where you thought one particular drive would be the best option only to discover that’s not the case. For example, for long linear drives, especially those with heavy mass, our engineers recommend an omega drive. For short span linear drives we would recommend zero backlash pulleys for the most accuracy and highest repeatability but are these rules appropriate for every application? Not necessarily.
There are several factors to consider, of which we could probably write a book, but since we like when you call us for advice, we’ll just briefly outline these factors below. Ultimately, if you have any doubt about the belt sizing requirements it is best to let a timing belt expert calculate your linear drive.
This is a good place to start. If you are sizing your drive to the load rather than to the motor then your need to know your carriage mass and coefficient of friction of the supporting rails. Depending on the type of drive, you may also need to consider counterweights, drive angle and back bending. Ultimately, the timing belt must be able to support the maximum load of the system without stretching or breaking. Make sure to choose a timing belt with a large enough tooth and width to handle your expected load.
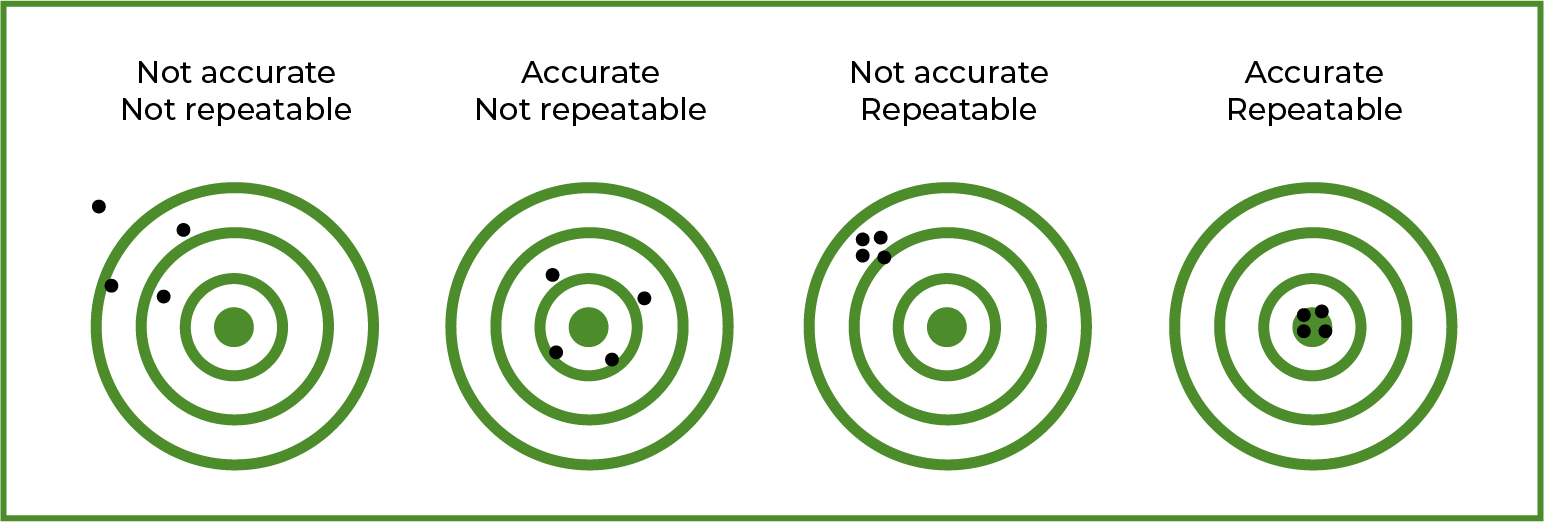
In the simplest terms, the accuracy refers to the tolerance of the back and forth motion. Repeatability refers to how closely the timing belt returns to a set point. BRECOflex has a formula for evaluating static repeatability. Considerations within this formula are elongation of the belt under static or dynamic forces, length tolerance consistency of the belt, and drive pulley backlash. See more about repeatability here.
The maximum speed, peak torque and peak braking torque of the system will affect the choice of timing belt. Higher speeds require a timing belt with a higher tooth shear strength to maintain accuracy and prevent skipping.
Speed: Timing belts are designed to operate at specific speeds, and exceeding this limit can lead to premature wear and damage to the belt. Additionally, the speed of the linear drive can impact the accuracy and repeatability of the system, so it's essential to choose a belt that can handle the required speed range.
Torque: The timing belt must be able to handle the required torque range while maintaining accurate and repeatable movement. If the motor generates too much torque, it can cause the belt to slip. Conversely, if the motor can't generate enough torque, the belt may not be able to move the object efficiently along the linear path.
Breaking: When the linear drive stops, it generates a force that opposes the motion of the belt. This force can cause the belt to elongate, which can lead to inaccuracies and reduced performance.
A linear drive timing belt capable of high load capacity with outstanding settling time and accuracy is the move-series open ended timing belt.
Tooth Profile: The tooth profile of the timing belt affects its performance. You can use both English and metric pitch timing belts but some will be more appropriate for your application than others depending on the level of accuracy you require. BRECO, the parent company of BRECOflex developed the AT tooth profile which has become the industry standard for accuracy. The AT pitch has half the backlash of the T pitch timing belt. Pairing an AT pitch timing belt with a zero backlash pulley will yield the best repeatability.
How hard can it be to determine belt length? Just use a ruler, right? WRONG! If you want the timing belt to work correctly and last a long time, proper measurement is key.
Length: The length of the timing belt is determined by the size of the drive and the distance between the two pulleys or fixed points in the linear drive system. For example, to calculate the length of the timing belt from pulley to pulley, the total length of the timing belt should be equal to the sum of the pitch circle diameters of the two pulleys. That’s a starting point but there is more to it than that. What is the pitch of your timing belt? How many teeth are in each pulley? What is the load capacity? Once you have all of that worked out, you need to determine the proper pretension.
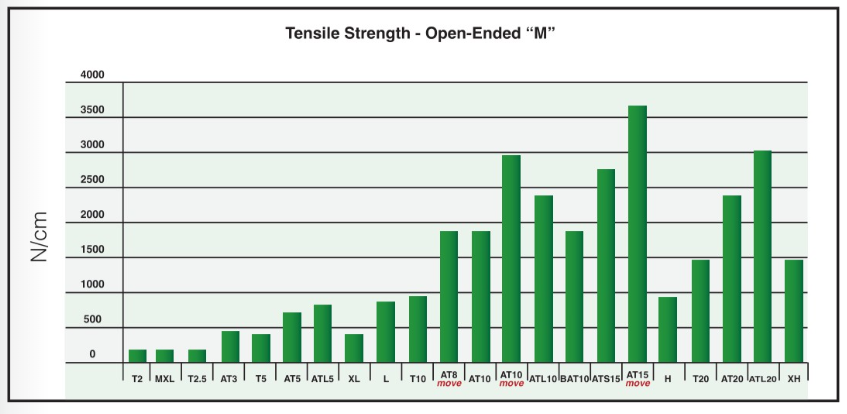
Pretension: The timing belt must be tensioned properly to ensure accurate and reliable performance. Tensioning clamps and tensioning idlers will assist in achieving profile pretension. Pretension is based on the pitch, width and construction of the timing belt. Linear drives use open-ended M timing belt construction and will use 100% of the force in pretension based on the maximum allowable tensile strength of the belt (N/10mm belt width). You can find these values in the specification charts of our B212 catalog or by using the SM5 Tension Meter and App for iOS or Android.
Using a Linear Drive Calculations Program will help you organize the data in one place to that an applications engineer can calculate the proper belt size thus guaranteeing that you purchase the right timing belt.

Temperature, humidity, static, exposure to chemicals and abrasive materials also have to be taken into consideration. BRECOflex polyurethane timing belts are resistant to water, simple oils, greases, fats, benzene and to some acids and bases. They can withstand a standard temperature range of 0°C to 80°C. There several types of polyurethane for the manufacture of timing belts that are made to accommodate many environmental factors.
By considering these factors and selecting the appropriate timing belt, you can ensure that your linear drive system operates smoothly and reliably. Contact our engineering department to speak to an expert about your project. Engineering support is always free and can save you time and money in the long run.